
Active and Passive Voice: A Clear Guide with 10 Examples
Understanding Voice in English Grammar
In English, some sentences feel more engaging than others. Have you ever wondered why? It might have something to do with voice.
Are you familiar with voice in the English grammar? Voice generally refers to a form of verb that describes the relationship between the doer and the receiver of the action. It indicates whether the subject of the sentence performs as the doer or the receiver.
There are two types of voice in English grammar: active and passive voice. When a sentence is written in the active voice, the subject is the doer of the action. On the other hand, a sentence is in the passive voice when the receiver performs the action.
Active and Passive Voice Explained
The active and passive voice are two important parts of learning the English grammar, because they are useful in determining the function of the subject in sentences. Read through this text as we discuss the roles of active and passive voice and which should be used better.
Structure
Active voice: doer of the action + verb + direct object
Mary is checking her email.
Doer verb direct object
Passive voice: direct object + verb + doer of the action
An email is being checked by Mary.
Direct object verb doer of the action

Active Voice
The active voice in grammar denotes that “the doer comes first.” This means that the subject performs the action in the sentence. Sentences in the active voice are clear, concise, and emphatic.
Example 1: The woman is looking after her children.
In this case, you can analyze the sentence by asking the question “Who is doing the action?” It’s the woman. So in this sentence, the woman is the subject and therefore does the action.
What is the action? (looking after her children)
Who is doing the action? (the woman)
The woman (subject) is looking after (verb) her children.
Example 2: You must have taken my purse accidentally.
In the sentence, who is doing the action, or who has taken the purse? It’s “you.” The subject “you” does the action. What is the action? It’s “taken my purse accidentally.” In this case, we can ask “What happened?”
You (subject) must have taken (verb) my purse accidentally.
Passive Voice
In the passive voice, the doer of the action is not the subject anymore. The subject in the sentence is the one that is being done, or something that is being acted upon by the verb. Clearly in the passive voice, the doer is now the receiver of the action.
Example 1: Alexie was kidnapped by unknown men.
The example sentence indicates that the subject is being acted upon by the verb. Notice that the doer of the action is not the subject.
Alexie (subject) was kidnapped by unknown men (doer of the action).
Who did the kidnapping? (unknown men)
Who was kidnapped? (Alexie)
Example 2: The students are being scolded.
In the sentence above, “the students” is the subject but not the doer of the action. Who, then, is the doer of the action? In this case, the doer of the action is not stated but is embedded. Technically, if we analyze the sentence, we can assume that the doer of the action could be the principal, the teacher, or somebody from their school.
The passive voice can stand independently even without mentioning who the doer of the action is.
Difference between the active and passive voice
Active Voice | Passive Voice |
The active voice has a direct, clear, and strong tone. | The passive voice has an indirect and subtle tone. |
It does not require a linking verb to make sense. | The passive voice uses a linking verb followed by a past participle to emphasize the meaning. |
It focuses on the doer of the action. | It focuses on what is being done in the sentence. |
The active voice denotes that the subject is the doer of the action. | The passive voice denotes that the subject is being acted upon by the action. |
The doer of the action is always mentioned. | The doer of the action can be embedded. |
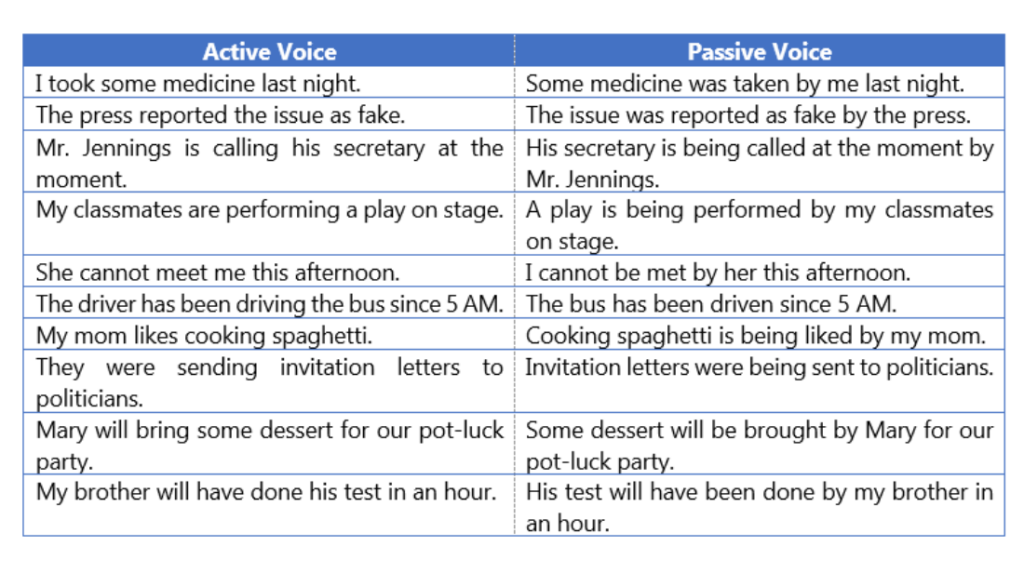
Examples Sentences in the Active and Passive voice
How to convert active voice to passive voice
To convert a sentence from the active to the passive voice, you need to shift the focus from the subject performing the action to the object receiving the action.
In the active voice, the sentence typically has a structure where the subject performs an action on the object. For example, in “The teacher explains the grammar,” “the teacher” is the subject performing the action, and “the grammar” is the object receiving the action.
To change this to the passive voice, you first make the object of the action the new subject of the sentence. Next, use a form of the verb “to be” that matches the tense of the original sentence, followed by the past participle of the main verb. Finally, you can include the original subject (now known as the agent) at the end of the sentence if needed.
So, the active sentence “The teacher explains the grammar” becomes “The grammar is explained by the teacher” in the passive voice. Here, “the grammar” is now the subject of the sentence, “is explained” is the passive construction, and “by the teacher” indicates who performed the action.
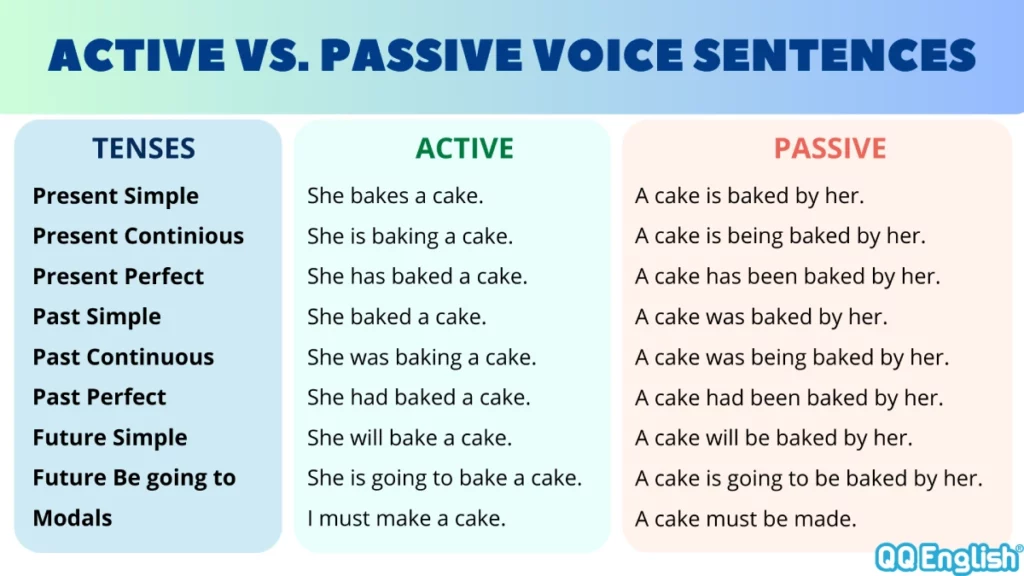
Active and Passive Voice: Rules in Verb Tenses
Here are the tense forms in passive voice that are rarely used:
Future Perfect:
- Active: She will have baked a cake.
- Passive: A cake will have been baked by her.
- Reason for rarity: The Future Perfect tense is used to describe actions that will be completed by a certain point in the future. Its passive form is rarely used because such constructions sound cumbersome and are complex for everyday conversation.
Past Perfect in passive voice is also less commonly used than its active form:
- Active: She had baked a cake.
- Passive: A cake had been baked by her.
- Reason for rarity: Although this form is more common than Future Perfect, it is still less frequently used because speakers often prefer active constructions to describe past actions.
Future Perfect Continuous and Present Perfect Continuous have hypothetical passive forms, such as “will have been being done” and “has/have been being done.” However, these forms are so complicated and awkward that they are virtually never used in speech or writing.
In English, the passive voice can’t be formed in certain tense forms due to the complexity of expressing ongoing or continuous actions in a passive structure. Here are the tense forms where passive voice is not used:
Future Continuous:
- Active: She will be baking a cake.
- Explanation: The Future Continuous tense describes an action that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. In passive voice, it’s challenging to convey this ongoing process because the focus is on the action being performed rather than the action itself. Therefore, this tense does not have a passive form.
Present Perfect Continuous:
- Active: She has been baking a cake.
- Explanation: The Present Perfect Continuous tense describes an action that began in the past and is still continuing or has recently stopped. Creating a passive form for this tense would involve complex and rarely used constructions like “has/have been being,” which are not standard in English. As a result, this tense is not used in the passive voice.
Past Perfect Continuous:
- Active: She had been baking a cake.
- Explanation: Similar to the Present Perfect Continuous, the Past Perfect Continuous describes an action that was ongoing in the past before another action occurred. The passive voice for this tense would require forms like “had been being,” which are awkward and generally avoided in English, making the passive form impractical.
Future Perfect Continuous:
- Active: She will have been baking a cake.
- Explanation: This tense describes an action that will have been ongoing up to a certain point in the future. The passive construction would be even more complex and cumbersome, involving “will have been being,” which is not used in standard English. Therefore, there is no passive form for this tense.
Active and Passive Voice: Rules in Pronouns
There are certain rules to convert active voice to passive voice. We make sure that the tenses are correctly labeled and used in sentences. At the same time, the pronouns to be used must also be appropriate to the sentence.
Active Voice | Passive Voice |
I | Me |
You | You |
We | Us |
He | Him |
She | Her |
It | It |
They | Them |
Key Points to Remember about Active and Passive Voice
- Always remember to interchange the subject when converting the active voice to passive voice.
- To better emphasize the doer of the action in the passive voice, use the preposition “by”.
- Remember to use the linking verbs and the past participle in the passive voice.
- No need to use linking verbs in the active voice.
- The main verb in the active voice is changed to a participle in the passive voice.
- Observe that the active voice must have a direct object to change it to the passive voice.
- In academic writing, it is appropriate to use the active voice.
Test Yourself!
Try to change the following sentences into active and passive voice.
- They are preparing their breakfast.
- She will judge the competition on Monday.
- The apples were being thrown to the trash bins.
- John was hit by a car.
- They make some beautiful decorations.



