An Overview of the 12 Tenses in English: Pay Attention to These Reflective Insights!
Introduction
Have you ever wondered about the difference between “I read a book” and “I am reading a book” or maybe “I watch TV,” “I watched TV,” and “I will watch TV”? They are easy to utter, yet difficult to analyze, particularly their tenses.
Many language learners find it difficult to study tenses in English despite their best efforts. They consistently misuse, misunderstand, and misapply the tenses in English even in their speaking practices. This situation is inevitable, especially for language learners who have difficulty understanding and applying the tenses.
For some language learners, tenses are less important and emphasized as long as the meaning of the statement they want to convey is clear and comprehensible.
However, it is better to be more familiar and conscious of the sentence construction with correct tenses to have a more appealing statement. It is also more appropriate than relying solely on the meaning of the context.
Of all the parts of speech, the verb is the most complicated. It has a lot of considerations. Tenses are not an exception. Did you know that tenses in English are the most important part of the language? They play a major role in getting the meaning of sentences
What are the tenses in English and why do we study them?
Simply, tenses essentially express the timing of a specific action at a particular period. The three main tenses in English verbs are the Past, Present, and Future Tenses. If you want to talk about something in the past, you can’t use a tense that is in the future or the present. The same is true with other things. You cannot use a tense in the past if you are talking about something at present or a plan in the future.
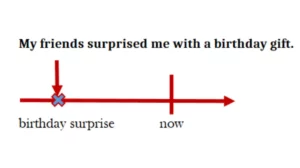
The Past tense talks about actions that were done permanently in the past. For example, “My father walked to the supermarket yesterday.” This sentence happened at a past time and it is already finished.
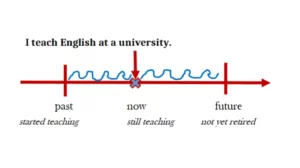
The Present tense talks about actions or events that are permanent. It also talks about habits and routines. For example, “He drinks a can of beer before going to bed every night.” The doer of this action regularly drinks, and that is every night.
Some other uses of the present tense are to show scientific, mathematical, geographical, and other facts. For example, “Mount Fuji is located in Japan.” This is a geographical fact stating the location of Mt. Fuji. Another example is “Jupiter has many moons” which is a scientific fact.
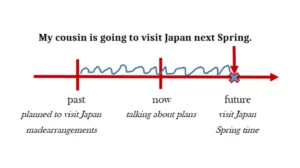
The Future tense talks about actions that will be done in the future. This expresses plans or predictions about a specific point in time in the future. We use “will or be going to” to express a future plan. For example, “I will visit my friend at the hospital after work today.” Another example is “My cousin is getting married next month.”
will vs be going to
Generally, both expressions are used in the future but they have slight differences. “Will” is used for sudden or unplanned actions. It means the doer of the action just decided to do something. On the other hand, “be going to” is used for predictions or pre-arranged plans.
Why do we study tenses in English in the first place? This is a question that is not that difficult to answer. We study tenses because we want to be clearly understood, so we have to observe the correct tense when expressing our ideas, our opinions, our sentiments, and other things. Without using the correct tense, the meaning we intend to convey is not clear.


Introducing Regular and Irregular verbs
Verbs are complicated. They have various conjugations to form a correct sentence. In order to make a grammatically correct sentence, proper usage of verb tenses is necessary. To use a correct verb, it is important to know that there are regular and irregular verbs in the English language.
Regular Verbs are verbs that have a fixed ending suffix. They do not change their forms when used in the past tense. For example, play – played, reach – reached, dance – danced, jog – jogged. Regular verbs usually end in “-ed,” and “-d.” For verbs ending in a consonant preceded by a vowel, the ending consonant is doubled and added with the common suffix –ed.
Irregular verbs are verbs that change their forms when used in the past tense. The spelling usually changes, but other irregular verbs do not change their spelling. For example, the verb “teach” is changed to “taught” when used in the past; “seek” becomes “sought,” “buy” becomes “bought,” “write” becomes “wrote” in the past, and “written” in its past participle, etc.
Irregular verbs don’t end in the suffix –ed or –d. Their forms are changed in the past and when used as past participle.
Some examples of Irregular Verbs can also be found on this page.
Please note that the be-verb “am” also has different forms: am, was, and been.
Other Tenses in English for Your Perusal
- Continuous Tenses – they express actions that are temporary and continuing. They are also called the progressive tenses in English.
- Present Continuous – actions that are happening at the moment.
Example: I am studying English.
- Present Continuous – actions that are happening at the moment.
- Past Continuous – actions that were happening at a particular point in the past.
Example: He was reading a text message when his mom called. - Future Continuous – actions that are expected to be happening at a specific time in the future.
Example: I will be traveling to New York at 4:00 this afternoon.
- Past Continuous – actions that were happening at a particular point in the past.
- Perfect Tenses – these tenses in English talk about actions that are completed at a particular point in time but have connections to other points in time.
- Present Perfect – actions that are completed in the past but are connected to the present time.
Example: The manager has arrived in the office.
- Present Perfect – actions that are completed in the past but are connected to the present time.
- Past Perfect – actions that have been completely finished in the past.
Example: Mr. Wellington had distributed relief goods during his administration.
- Past Perfect – actions that have been completely finished in the past.
- Future Perfect – actions in the future that are expected or anticipated to happen.
Example: I will have finished my report by 10:00 PM tomorrow.
- Future Perfect – actions in the future that are expected or anticipated to happen.
- Perfect Progressive Tenses – these tenses in English express actions that were, is, are, and will be in progress and have not been completed yet. Meaning, the progress is going on.
- Present Perfect Progressive – this talks about actions that are ongoing at the present time.
Example: I have been taking pain relievers.
- Present Perfect Progressive – this talks about actions that are ongoing at the present time.
- Past Perfect Progressive – expresses actions that started in the past and were completed until another action in the past.
Example: They had been receiving spam calls for five consecutive days before reporting it to the police.
- Past Perfect Progressive – expresses actions that started in the past and were completed until another action in the past.
- Future Perfect Progressive – refers to actions that will be continuing until it is completed at a specific point in the future.
Example: My cousin will have been living in Taipei for ten years by the end of next Spring.
- Future Perfect Progressive – refers to actions that will be continuing until it is completed at a specific point in the future.

What You Need to Know About Tenses in English
The tenses in English are sometimes confusing for language learners. Tenses in English are crucial for conveying the timing of actions and events. For you to be guided, we have compiled a list of key insights that you need to know about tenses in English.
- Each tense has a unique structure and usage that impacts the meaning of a sentence.
- There is always a difference in meaning for each tense in English.
- Tenses in English are clearly expressed in timelines.
Past tense
Present tense
Future tense
- The verbs in the past tense vary and depend on whether they are regular or irregular verbs.
- Do not confuse “will” and “be going to” for the future because “will” is for immediate decisions or unplanned actions while “be going to” is for predictions and planned actions.
- The past, present, and future tenses in English have other sub-tenses: continuous or progressive tenses, perfect tenses, and perfect progressive tenses.
- Be-verbs, auxiliary verbs, and modal verbs are often used in the simple tenses in English.
- The perfect tenses in English always have past participles, regardless if it is present, past, or future.
- Some students utter sentences without being aware of the correct use of tenses.
- Present tenses and present continuous tenses in English are often interchanged ignoring the meaning of the sentence. For example, “I am reading a book” or “I read a book.”
- Simple tenses are for permanent actions while continuous tenses are for temporary actions.
- There are confusions with learners’ use of plurality or singularity in sentences. The subject-verb agreement is less observed. For example, “He bring the book,” or “We uses the computer.”
- Students may talk about the past using the present tense. For example, “I am a dancer during my elementary days.”
- Irregular verbs are often misused. Example “drunk – drunked” or “think – thinked.”
- The sentence with a correct tense emphasizes the meaning it conveys, and is clearly understood.
The tenses in English are confusing, but they make sentences meaningful. Observing the correct use of tenses in English is important to clearly express your intended point. Use a timeline to better understand each tense. With knowledge about the tenses in English, any language learner can gradually improve their language skills.
Why do Tenses Matter?
Learning tenses in English may seem like a challenge, but it’s the key to unlocking clear and confident communication. Each tense acts like a time machine, allowing you to accurately express when things or actions happen. With little and constant practice, you’ll be conveying your thoughts and ideas confidently and smoothly.