
Learn the Past Tense in English: 5 Tricks to Make It Stick
“What did you brought for me?” Is this a grammatically correct sentence? What if you heard someone say, “I drinked my coffee this morning?” These are only two of the many errors language learners often commit when using the past tense in English.
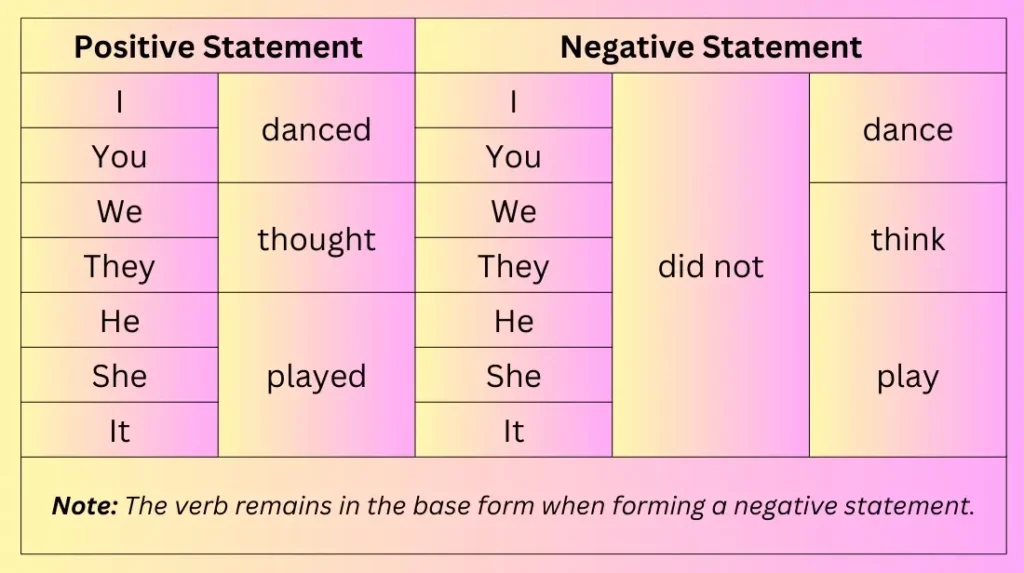
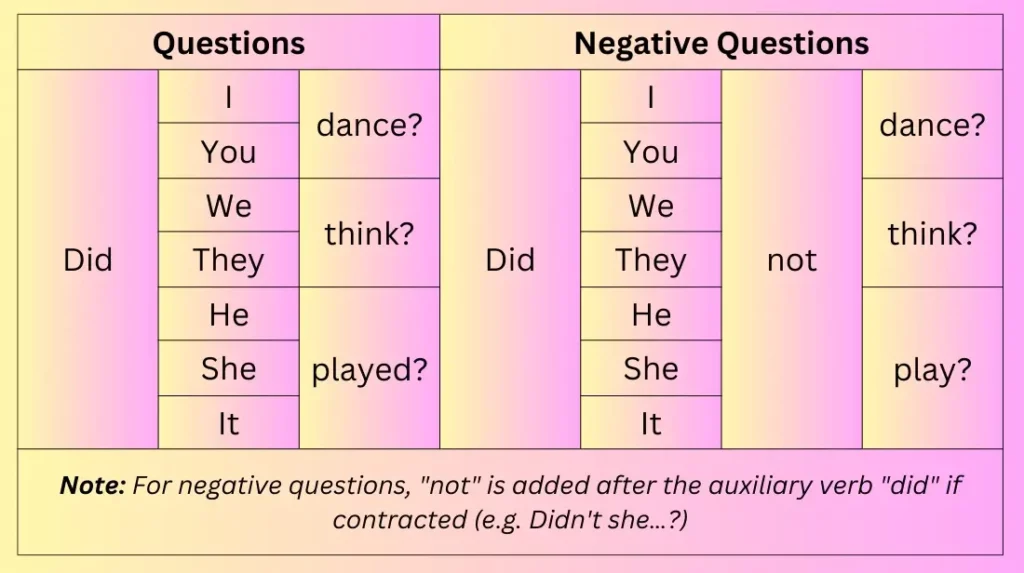
The past tense in English is more complex than the present tense because it involves a lot of verb changes when conjugated. The form of the verb changes depending on which type of verb is used: regular or irregular verbs.
It is easy to identify the past tense of a regular verb. Regular verbs are only added with the suffix –ed. Irregular verbs on the other hand are more complicated because you must be knowledgeable of the correct conjugation when changing a verb in the present form to its past tense and past participle.

Common errors in the use of the past tense in English occur in both writing and speaking. Errors are inevitable, so it is important that you know how to use the past tense in English correctly.
In this article, we will focus more on the simple past tense in English and discuss how it should be used appropriately. We will also share some ways to learn it effectively. So stay connected as we dive into the world of the past tense in English.
The simple past tense in English
The simple past tense talks about an action that is already finished and does not have any relationship with the present or future. The action was done at a particular time in the past.
For better understanding, here is a timeline for your reference.
Example:
My parents painted the wall yesterday.
What was the action? – painted
When did it happen? – yesterday
In this case, the verb “painted” is in the past because it was already finished. “My parents” are no longer painting at this time. It only happened “yesterday” so it is done now. However, note that the example sentence above has a time marker: yesterday. It just simply means that the action happened yesterday.
For past tenses in English with no time markers, here is an example.
I drove a car to the airport.
In this case, the verb “drove” is in the past because basically, it is the past tense of the verb “drive.” By simply looking at the sentence, it is understood that the action happened in the past and it is already finished.
Common learner errors
- Learners often treat irregular verbs as regular verbs. For example, drink – drinked, think – thinked.
- The auxiliary verb “did” is sometimes added to the past tense of the irregular verb. For example, “He did wrote an article about terrorism.”
- In speaking, sometimes the suffix –ed is not clearly heard. For example, “She talk with her manager.”
- Some learners produce sentences with full verb patterns by adding auxiliary verbs to modals, which is inappropriate. Say for example, “I didn’t can swim.”
- One irregular verb is sometimes misinterpreted and perceived by learners with one structure. For example, “drunk – thunk.”
Why is learning the past tense in English important?
Learning all the tenses in English is important to convey your message appropriately and effectively. If you are not aware of the tense you are using, your listener might be confused especially when talking about time frames.
For most language learners, it is difficult to use the correct tenses in their sentences. However, there are ways to learn it and apply it in conversations effectively. It is crucial that you learn these ways to have meaningful and effective communication with your interlocutors.
At the same time, your listener will easily determine that what you are talking about happened in the past and he will imagine a specific action in the past. By this, learning the past tense in English is important for effective and successful communication.
How to Learn the Past Tense in English in 5 Easy Ways?
Learning the past tense in English can be quite challenging, but it can become much simpler with determination and the right approach. Here are 5 easy and effective ways to learn the past tense in English.
- Read stories, biographies, or history texts.
Stories are usually written in a past setting as well as biographies and some historical facts. If you read these kinds of texts, you will emerge familiar with words that are used in the past tense in English.
If you encounter unfamiliar words and you are unsure if it was written in the past tense or not, you can check the context or search for them on the internet. By doing this, reading regularly can help you quickly learn the past tense in English.
- Familiarize the forms of regular and irregular verbs.
Make a list of regular and irregular verbs or check them here. With your list, you can identify the form of the verb that you will use in sentences. Familiarizing yourself with the correct verb forms is one way to appropriately convey your message.
It is sometimes confusing that irregular verbs have different forms when conjugated, but if you are willing to progress quickly, familiarize yourself with them until you memorize them.
- Look for grammar quizzes on the internet.
There are various grammar quizzes on the internet that tackle all the tenses especially the past tense in English. You can test yourself for free and then check where you had an error. These quizzes vary per level of difficulty so choose the ones that are appropriate for your language level.
- Practice using the past tense in English sentences.
Constant practice does not necessarily mean perfecting the past tense in English, but it is a great help to improve your sentence construction skills. With regular practice, you will be more conscious of your tenses in sentences.
Constant practice of using the past tense in English can improve your communication skills. Don’t worry, you will get used to it.
- Have a casual conversation with a friend or family member.
It is always fun to share sweet and fun conversations in English with a friend. You can talk with them or share some exciting activities that you did yesterday or last weekend. You can share stories or anecdotes about your experiences.
Having a casual conversation in English can enhance your conversational skills. You have the chance to express yourself confidently by observing the correct use of the past tense in English.
Active use and practice of the past tense in English makes you more confident and more comfortable in the language. Practice is the key.

Test Yourself
Identify whether the following sentences are correct or not. If not, correct the sentence.
- Stefanie take her dog for a walk yesterday afternoon.
- My mother told us to do the household chores.
- He is ill last week so he did not go to work.
- Are you at the party last night?
- Adams underwent surgery in Thailand.
- The attendees of the conference were glad to meet the speaker.
- The manager warn the employees about what happened in the elevator.
- Did you gathered the envelopes from the students?
- Who was with the children in the camp last year?
- Lady Ann thunk she would be suspended for joking.
Did you get all the correct answers? Check them out here.



